What is Vehicle To Vehicle Communication System?
Discover vehicle-to-vehicle communication and how it enhances road safety by enabling real-time data exchange between cars. Learn more to stay informed!
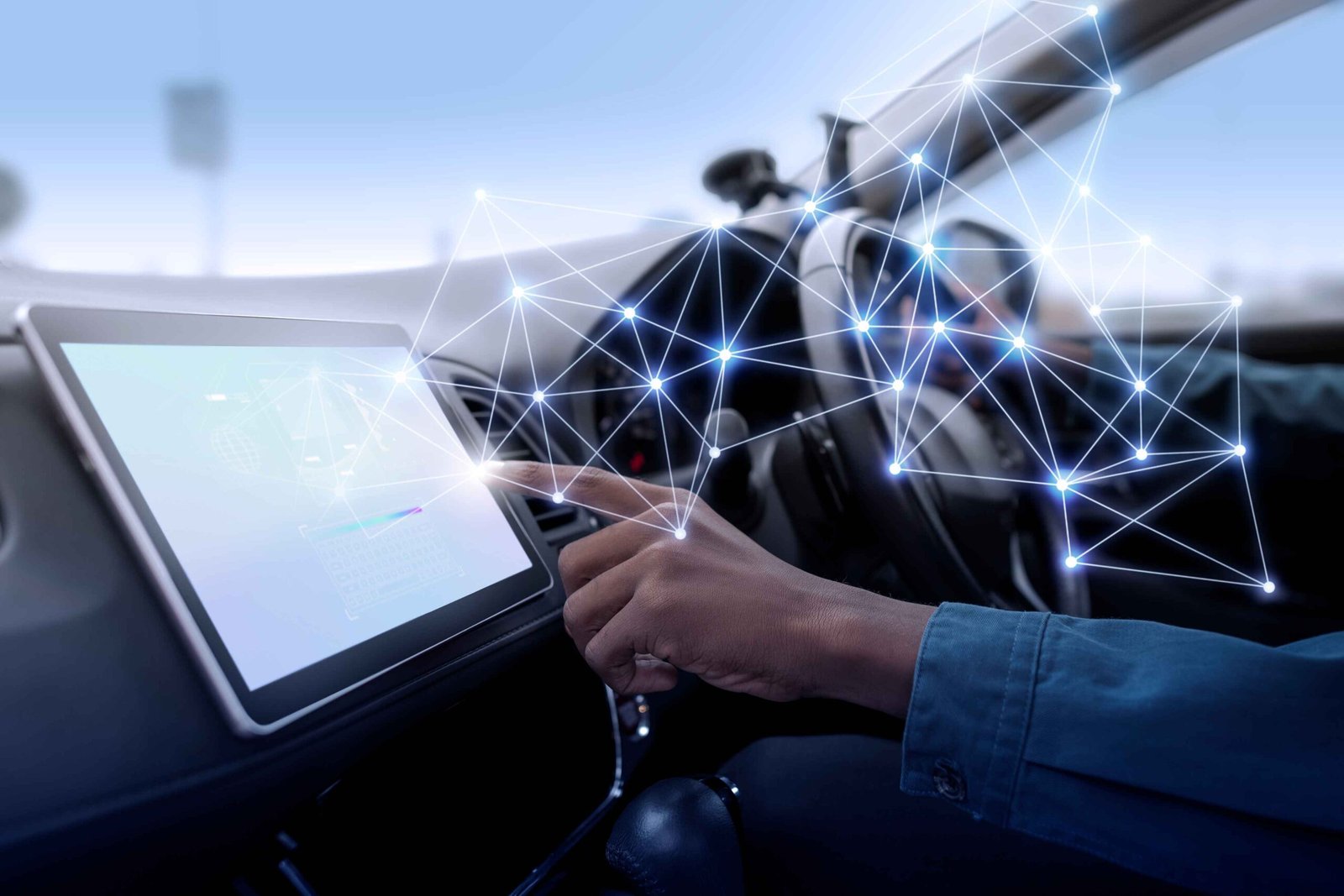

What if cars could “talk” with each other? That’s more or less what vehicle-to-vehicle communication enables. The goal of this unique technology is simple: to make driving safer, reduce traffic congestion, and improve road efficiency. Let’s explore how this system works, its components, and its potential to change how we drive.
Understanding Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication (V2V)
Vehicle-to-vehicle communication allows cars to exchange data, such as speed, location, and direction, so vehicles can anticipate each other's movements. V2V systems improve situational awareness in cases of blind spots, sudden stops, or limited visibility.
For example, if you suddenly hit the brakes, it sends a Basic Safety Message (BSM) to nearby vehicles quickly to reduce speed and avoid a collision. This communication occurs with less than 20 milliseconds of latency. Such rapid response is crucial to prevent accidents in fast-moving traffic.
Key Components in a Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication System
For the vehicle-to-vehicle communication system to work effectively, several key components need to come together:
1. Onboard Communication Units (OBUs):
These devices are installed in vehicles to send and receive data. The OBUs communicate information such as speed, direction, and location with other vehicles nearby. They use Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) or Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (Cellular V2X) technologies for data transmission.
2. Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC):
Using DSRC technology, vehicles can transmit data at 5.9 GHz over a distance of up to 300 meters. It helps cars to communicate in real-time and allows them to respond quickly to one another's movements.
3. Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (Cellular V2X):
Unlike DSRC, Cellular V2X uses 4G LTE and 5G networks for broader communication, specifically in urban areas. It supports Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I), Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P), and Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) communications.
4. Sensors and GPS:
Vehicles are equipped with various sensors such as radar, LIDAR, and cameras to detect obstacles or other vehicles in close proximity. The sensors along with GPS systems let the vehicle process both environmental data and V2V messages for timely decisions.

5. Cloud Integration:
Many V2V systems also use vehicle-to-cloud communication, where data is sent to the cloud for processing. This provides real-time traffic, weather, and road conditions for better safety and efficiency.
How Does Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication Work?
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication relies on Onboard Communication Units (OBUs) powered by the vehicle’s electrical system. These OBUs process data from sensors like GPS, radar, LIDAR, and cameras to track speed, location, and direction.
When sudden braking occurs, the OBU sends Basic Safety Messages (BSMs) with speed, position, and brake status. Nearby vehicles receive BSMs almost instantly through DSRC or C-V2X. This triggers alerts or activates systems like emergency braking in them. It communicates with the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) to adjust speed or position.
Vehicle-to-Cloud (V2C) and Vehicle-to-Network (V2N) Communication
Vehicle-to-Cloud (V2C) and Vehicle-to-Network (V2N) communication significantly extend the capabilities of V2V. These technologies help vehicles access data beyond what can be obtained through direct communication with other vehicles. Let’s discuss them briefly in this section.
| Technology | Description | Benefits |
| Vehicle-to-Cloud Communication (V2C) | Allows vehicles to send data to the cloud for processing and analysis.
The cloud provides real-time updates on traffic, weather, and road hazards. |
|
| Vehicle-to-Network Communication (V2N) | Connects vehicles to surrounding infrastructure such as traffic signals and smart road systems.
Enables dynamic traffic management, like adjusting signal timings. |
|
Together, V2C and V2N technologies allow for safer, more efficient roadways by utilizing data from vehicles, infrastructure, and the cloud.
How Vehicle Communication Systems Improve Safety and Efficiency
The most significant benefit of vehicle-to-vehicle communication is safety. Studies suggest that 79% of crashes can be prevented using V2V systems. These are a few other important safety features of V2V:
- Collision Avoidance: V2V systems help prevent rear-end collisions by alerting drivers when a vehicle in front suddenly brakes.
- Intersection Safety: V2V systems warn drivers about cross-traffic when approaching intersections. This reduces the likelihood of accidents in high-risk areas.
- Blind Spot Detection: The system helps drivers detect when another driver changes lanes to avoid accidents.
- Efficiency: V2V allows vehicles to adjust their speed and spacing in real time to reduce congestion. This minimizes stop-and-go traffic, resulting in smoother commutes.
- Traffic Optimization: Vehicle-to-network communication optimizes traffic flow by dynamically adjusting traffic signals to reduce delays at intersections.
The Future of Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication
Looking ahead, the potential for vehicle-to-vehicle communication is huge. Here are two main technologies that are expected to be seen more in V2V communication:
1. Interconnected Networks
The combination of Cellular V2X, V2N, and V2C will create a fully interconnected network. Vehicles, infrastructure, and cloud-based services will work together to make roads safer and more efficient.
2. Li-Fi in V2V Communication
Li-Fi is another interesting technology that V2V will adapt more of. The reasons are quite clear: Li-Fi utilizes invisible light waves for fast, secure data transmission, and improves on-road communication. With its low interference and efficient use of existing lighting, Li-Fi can enhance safety and efficiency in connected transport networks.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the future of transportation isn’t just automated; it’s interconnected. Vehicle-to-vehicle communication is a key component of safer, smarter, and more efficient roads. And as V2V systems evolve, technologies like Li-Fi will transform the future of connected mobility. To equip your V2V systems with the power of Li-Fi, get in touch with our expert now.
V2V communication allows vehicles to exchange data such as speed, location, and direction to improve safety and efficiency. It helps vehicles anticipate each other’s movements and react instantly to prevent accidents.
V2C involves vehicles sending data to cloud-based servers for processing, offering real-time updates on traffic, weather, and road conditions. Unlike V2V, which focuses on vehicle-to-vehicle data exchange, V2C enhances situational awareness through broader data aggregation.
V2N connects vehicles to surrounding infrastructure, like traffic signals and road signs, enabling smart traffic management. It helps optimize traffic flow and safety by dynamically adjusting signals and responding to real-time traffic data.
V2V systems are designed with strong encryption and security protocols to protect data transmission. However, ongoing advancements in cybersecurity are crucial to safeguard against potential vulnerabilities and ensure data privacy and system integrity.
Recent articles

Categories
See some more...